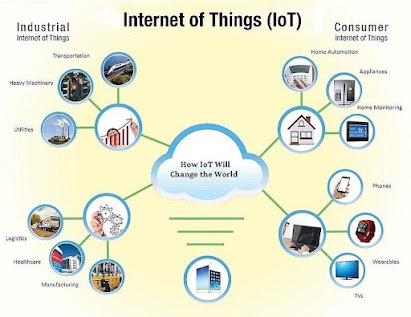
INTERNET OF THINGS AND APPLICATIONS
Smart Home and Office

Smart home applications with the use of smart sensors are becoming popular now. Any smart device can be configured and connected to the internet and control using simple mobile application.
Smart Door access control system
Smart locks and door access systems are one of the most popular and cost effective solutions of Internet of Things. Smart locks are easy to implement and control using a web interface or Smartphone application.
Integration with RDIF tags, smart door accessing systems can be securely implemented. Users can grant access to the doors using mobile app and lock again once the person leaves the premises.Annual flagship summit alongside its first-ever international summit to showcase how Tencent's industrial internet and cloud expertise help businesses succeed globally in digital transformation
Tencent Cloud and Smart Industries Group (CSIG)'s leaders and experts, as well as strategic business partners, joined together to share their visions for the future of cloud, immersive convergence, Web 3.0 and other detailed strategies to accelerate international growth, while showcasing a diverse portfolio of business success stories on integrating cloud solutions into gaming, fintech, social communications, entertainment, e-commerce, and other verticals.
Industrial Internet: Propelling Collective Success across Multiple Industries
As Tencent looks to further create sustainable growth, Dowson Tong, Senior Executive Vice President of Tencent and President of CSIG, underlined 'Immersive Convergence' as an important strategy and roadmap for the company's future pipeline, "The convergence between our physical and virtual worlds is transforming the way we live. Leveraging our technologies and connectivity solutions, we will continue driving innovations for enterprises to boost their digital competitiveness."
Tencent has been spearheading the evolution of the Industrial Internet, creating innovative enterprise solutions to enhance performance and bring business value. Today, Tencent's enterprise communication platform, WeCom connects over 10 million organizations to 500 million Weixin/WeChat active users. Tencent's cloud conferencing tool, Tencent Meeting/VooV Meeting supports more than 300 million users worldwide, while its blockchain-powered e-signature service supports millions of users to complete signing a contract in only 15 seconds. More than three million of developers have also used Tencent CloudBase to create mini programs, deploy web applications and develop mobile applications.
Visit:
Abstract Submission: https://x-i.me/sacon
Conference Reg: https://x-i.me/sareg1
Award Nomination: https://x-i.me/iotnom
Award Reg: https://x-i.me/sares2
Member Nomination: https://x-i.me/iotmem
#internet#technology#automation#cloudcomputing#edgecomputing#protocals#dishwasher#5gNetworks#4gNetwork#technology conferences#